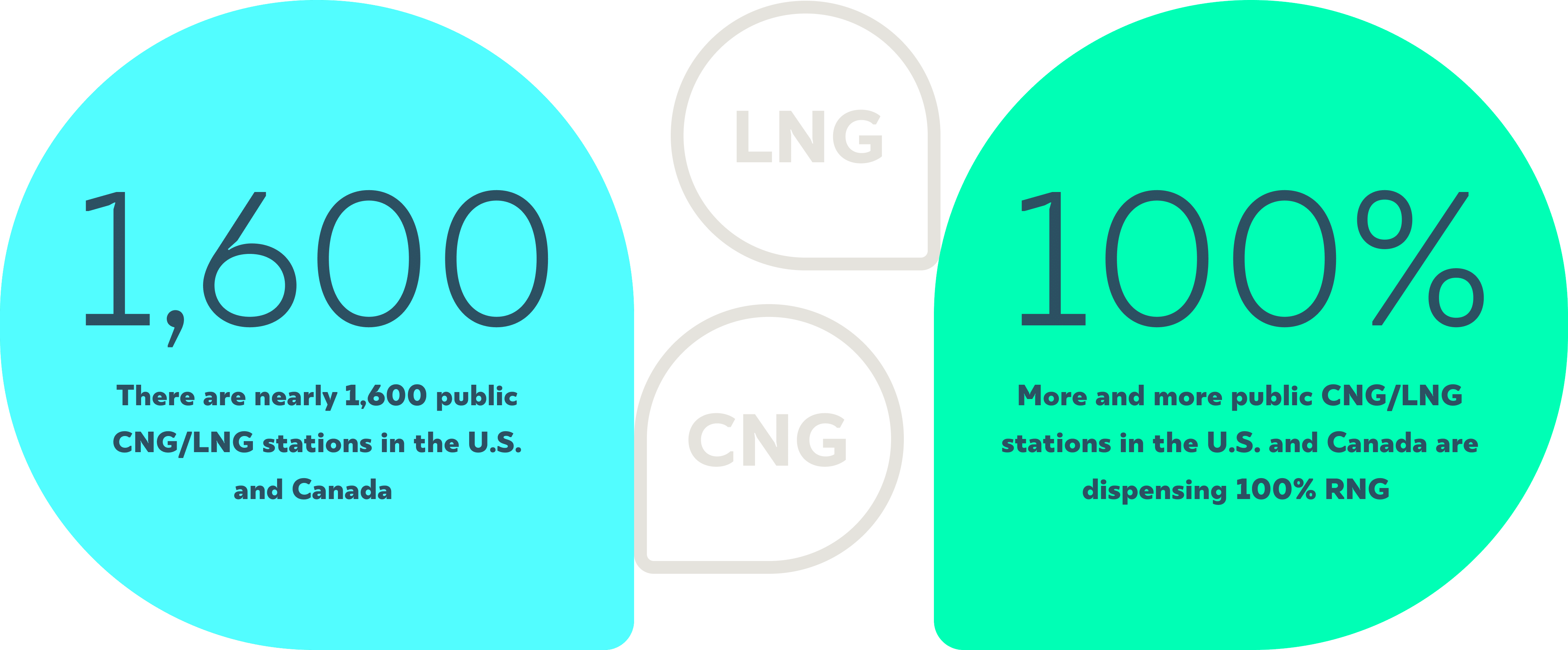
Natural Gas vehicle station counts continue to rise in the US, with stations now available on most highways and interstates. Whether a vehicle requires CNG, natural gas that is typically compressed at the station, or LNG, natural gas that is either liquefied on-site or trucked in from a liquefaction facility, today’s drivers have many more options for refueling than even three years ago.
Search the map below to find Natural Gas stations on your route:
NGV Station Types
Natural gas vehicles are fueled primarily at three types of stations:
Fast-Fill CNG, Time-Fill CNG, and LNG.
Need a natural gas station on your route?
If use of existing fueling infrastructure is not practical, convenient, or economical, it may be better to build a new CNG, LNG, or LCNG station. NGVA can connect you with member station builders across North America.
NGVA can connect you with member station builders across North America.
